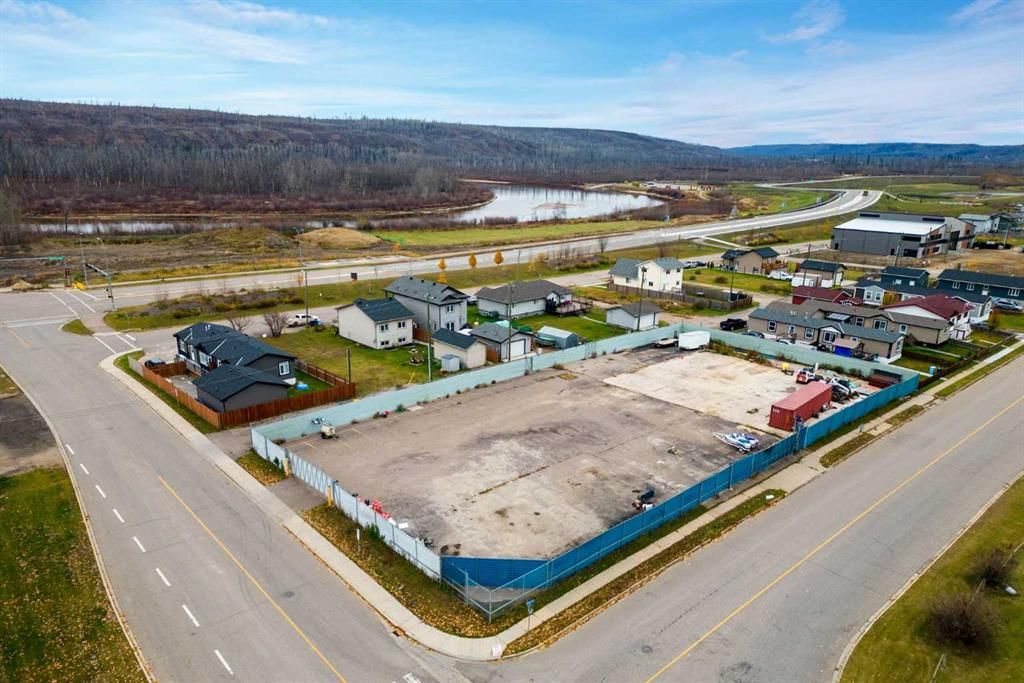
Yes. Industrial land can be converted to residential use, but it involves navigating zoning regulations, environmental concerns, and associated costs. With Fort McMurray experiencing growing housing demand, repurposing industrial spaces is becoming an increasingly viable solution.
This guide explores key considerations—zoning, environmental assessments, costs, and potential challenges—to help you assess the feasibility of such a project in Fort McMurray.
Industrial vs. Residential Land Use
Industrial land in Fort McMurray is typically zoned for factories, warehouses, and manufacturing facilities. These areas support commercial activities and heavy infrastructure.
Residential land, by contrast, is designated for housing, including single-family homes, townhouses, and apartment buildings. The zoning distinction determines what can be built and what activities are allowed.
Urban growth often brings residential developments into former industrial zones. While this shift can address housing shortages, converting industrial land requires careful consideration of legal, financial, and logistical factors.
Zoning Laws and Land Use Regulations
Zoning laws, set by local governments, define how land can be used—whether for residential, industrial, commercial, or mixed purposes. In Fort McMurray, industrial land cannot be used for residential purposes without undergoing a formal rezoning process.
Rezoning Process
Rezoning involves filing an application, undergoing public hearings, and receiving approval from local authorities. The decision considers city plans, infrastructure, and community needs. Challenges may include opposition from businesses, traffic concerns, and environmental risks.
Key Considerations for Conversion
Environmental Impact
Industrial land may have contamination from past use. Environmental assessments determine risks like polluted soil or water. Cleanup efforts can be expensive and time-consuming.
Infrastructure Needs
Industrial zones often lack infrastructure for residential use, such as roads, sewage, and water systems. Upgrading these can add significant costs and extend timelines.
Market Demand
Assess whether the area has demand for housing. A market analysis helps ensure the project is financially viable.
Challenges of Converting Industrial Land
Legal and Regulatory Barriers
Rezoning requires navigating complex regulations and addressing community concerns. Public hearings and opposition from businesses or residents can delay or derail projects.
High Conversion Costs
Costs include environmental remediation, infrastructure upgrades, and rezoning fees. While the potential value of residential land may be high, upfront expenses can be substantial.
Community Concerns
In Fort McMurray, businesses may resist the introduction of housing near their operations due to potential conflicts, such as noise or traffic congestion. On the other hand, residents may worry about the strain on local resources or an increase in population density. Addressing these concerns is key to ensuring successful project approval.
Alternatives to Full Conversion
Mixed-Use Developments
Mixed-use projects blend residential, commercial, and industrial spaces, balancing community needs and maintaining economic activity.
Adaptive Reuse
Repurposing industrial buildings for residential use—such as converting warehouses into apartments—can be cost-effective and environmentally friendly.
Final Thoughts
Converting industrial land to residential use in Fort McMurray requires careful planning, including understanding zoning laws, conducting environmental assessments, and evaluating infrastructure needs and market demand. While the process is complex, it can be a valuable endeavour in addressing the growing housing demand.
For expert guidance on navigating this process, contact Susan Lore or Tristan Parker at The Lore Group – Coldwell Banker United. They can help you assess the feasibility and guide you through each step of the project.